Skin/Melanoma Cancer Treatment:
Table of Contents:
1. Introduction:
As it is named, skin cancer starts in skin cells. Although there is a possibility to develop anywhere on the skin, it is most prevalent where the skin is exposed to the sun. Also, it is the most frequent sort of cancer. So, the 2 most common types of skin cancers are Basal cell carcinoma as well as squamous cell carcinoma . And these both may typically be cured with early detection and treatment.
Melanoma/skin cancer is a less frequent but more serious kind of skin cancer that, if left untreated. Consequently, it can spread to other body parts too. Talking about the vulnerabilities, sun exposure, a history of sunburns, fair skin, a family history of skin cancer, and a compromised immune system are all risk factors for developing skin cancer. Simultaneously, protection from the sun, avoiding indoor tanning, and routine skin inspection for changes or anomalies are all part of prevention.
In conventional allopathy, surgery and radiation therapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are available as treatments for skin cancer.
According to the biological pattern of cell division, new skin cells often develop when existing ones die or are injured. If this process doesn’t function properly, cells develop quickly, some of which may be abnormal cells. This group of cells could be a tumor, which if not identified and treated early enough could spread to surrounding tissues of your body, or noncancerous (benign), which don’t spread or harm.
2. Early Prevention through Ayurveda:
Ayurveda recommends several remedies that may help prevent skin cancer:
Use a Natural Sunscreen: Applying natural sunscreen could be protective your skin from harmful UV rays that can cause skin cancer. Ayurveda recommends using natural ingredients such as aloe vera, coconut oil, and sandalwood powder as sunscreen.
Amla/Indian gooseberry: This is rich in antioxidants and it can protect your skin from harmful UV rays. Consuming amla or applying it topically can help prevent skin cancer.
Turmeric: Curcumin, a crucial compound in turmeric, has anti-inflammatory as well as antioxidant properties to protect the skin from cancer-causing agents. Consuming turmeric in food or topical application is recommended.
Neem: Neem is rich in antibacterial, antiviral, and antioxidant properties. These can help prevent skin cancer. Applying neem oil consuming neem supplements may provide protective benefits.
Triphala: This is an Ayurvedic herbal formulation that contains three fruits namely Amla, Haritaki, and Bibhitaki. It has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that may help prevent skin cancer.
Gotu Kola (Brahmi): Gotu Kola is an Ayurvedic herb that has antioxidant properties to prevent skin cancer.
Guggul: This Ayurvedic herb has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can prevent skin cancer. Consuming guggul supplements has versatile benefits.
3. Which parts of the body does Skin Cancer Develop?
The regions of your skin that are exposed to the sun the most include your face (even lips), ears, neck, arms, chest, upper back, hands, and legs. In certain cases, the skin between your toes, beneath your fingernails, palms of your hands, soles, and in your genital area. As seen, there are some parts less exposed and more concealed areas where it might manifest.
Let us have a deeper insight:
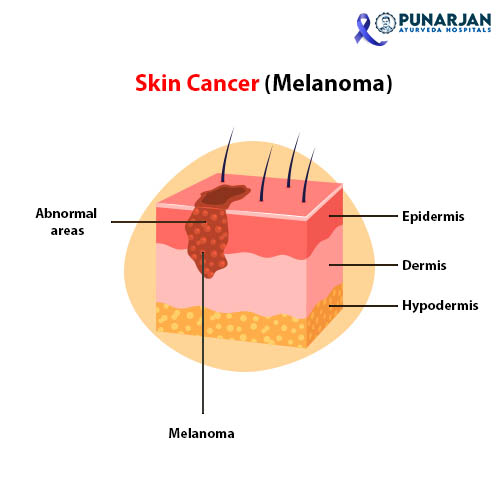
In fact, most skin cancers start in the epidermis (top layer of the skin). The epidermis consists of 3 major cell types.
Squamous cells:
These are flat cells that are found in the outer layer of epidermis. As new cells develop, they shed continuously. Therefore, Squamous cell carcinoma is the name of the type of skin cancer that can develop in these cells.
Basal Cells:
Below the Squamous cells, we can find basal cells. To replace the dead squamous cells, they divide, replicate, and finally flatten out. And, these cells travel higher up in the epidermis to become new squamous cells. Basal cell carcinoma refers to the skin cancer that develops in basal cells.
Melanocytes:
As the name defines, these are the cells responsible for producing melanin. It is a brown pigment that gives skin its color and shields it from some of the sun’s harmful UV radiation. Melanoma is the name for skin cancer that starts in melanocytes.
4. Symptoms of Skin Cancer:
If there is a change in your skin, usually a new growth or a change in an existing growth or mole, then it is the most prominent warning sign of skin cancer. This is a description of the symptoms and signs of both common and uncommon kinds of skin cancer.
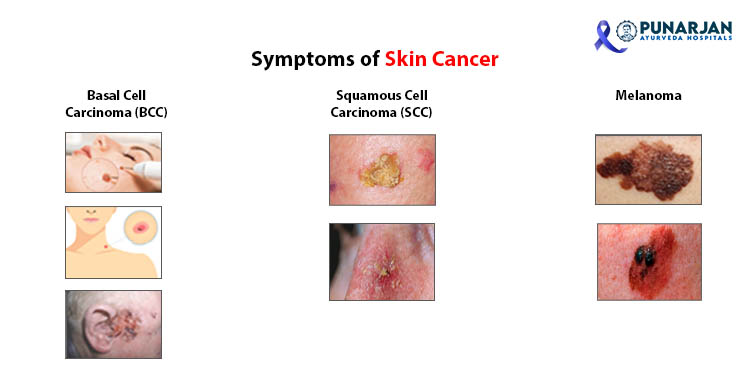
Symptoms of Basal Cell Carcinoma:
Sun exposed skin can most frequently develop basal cell cancer. It generally includes hands, face, arms, legs, ears, mouths, or sometimes bald places on top of your head. It is typical and normally doesn’t spread to other body areas, grows slowly in most people, and is not life-threatening.
- Basal cell carcinoma is characterized by a tiny or waxy lump on the face, ears, or neck.
- A flat, red, or brown lesion on the limbs or trunk.
- Skin patches that look like scars.
- Sores with depression, a crusty appearance, or frequent bleeding.
Squamous cell carcinoma
As already discussed, the skin on your hands, face and many parts of the body are regularly affected by squamous cell cancer because they are exposed to the sun. In addition, Mucous membranes and the genitalia are two more places where this skin cancer can develop.
Symptoms of Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
- A solid crimson or hard pink nodule.
- A scratchy, scaly lesion that may itch and bleed.
Symptoms of Melanoma:
Melanoma can get access to any part of the body without restrictions. Even your eyes and internal organs may develop it. In men, it’s common to find the upper back, whereas in women it’s usually the legs. It has the potential to spread to any part of your body. And, this type of skin cancer is the most dangerous.
Symptoms of melanoma:
- A lump or area on the skin with brown pigment.
- A bleeding mole changes size, or changes color.
5. What Causes Skin Cancer?
The basic cause of skin cancer is Ultra Violet Rays. The 2 main causes of skin cancer are UV rays exposure from the sun and you can even use UV tanning beds. Fortunately, if skin cancer is found early by your dermatologist, it has a high probability of being fully removed. Because, its development is frequently discovered by the doctor even at the precancerous stage, before it penetrates beyond the skin’s surface.
6. What are the stages involved in the growth of skin cancer?
Basal cell carcinomas can be staged using certain characteristics that are thought to put the cancer at a higher risk for metastasizing or recurrence. Check the following;
Basal Cell Carcinoma Stages:
- If the thickness of the tumor is more than 2 mm
- If it affects the skin’s lower dermis or subcutis layers
- Effect on the skin small nerves, ear or a lip with hair
- Cancer is given a stage when the TNM components and risk factors have been established. The criteria are categorized and assigned the numbers 0 to 4 for basal cell carcinoma staging. Based cell carcinoma has the following stages:
Stage 0:
Cancer found at this stage, also known as carcinoma in situ. And, it is limited to the epidermis (top layer of the skin) and has not penetrated further into the dermis yet.
Stage 1:
Stage 1 cancer of this type includes one or fewer high-risk characteristics. They are less than 2 millimeters in size (about 4/5 of an inch across), and have not yet spread to adjacent lymph nodes or organs.
Stage 2:
Any sized tumor with 2 or more high-risk characteristics is considered to be in stage 2. It is more than 2 cm in diameter and has not yet spread to adjacent lymph nodes or organs.
Stage 3:
Stage 3 cancer is defined to have progressed to one neighboring lymph node or the face bones without affecting other organs.
Stage 4:
Now, stage 4 cancers of this type can range in size. Probably, they have metastasized to one or more lymph nodes larger than 3 cm, and may have spread to the bones or other internal organs.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Stages:
Similar to basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma has some characteristics that increase the likelihood that the cancer may spread or recur, and those characteristics are frequently important in defining the stage of squamous cell carcinomas. These features consist of:
- Thickness of more than 2 mm
- Affecting lower dermis or subcutis layers of the skin
- Affecting the small nerves in the skin, ear or a lip with hair
Below are the 5 stages of Squamous Cell Carcinoma based on the TNM components;
Stage 0:
Cancer found at this stage is known as carcinoma in situ. It is limited to the epidermis and has not penetrated deeper into the dermis. Bowen’s disease of the skin is another name for this stage of squamous cell carcinoma. It manifests as red or pink scaly patches on skin that is frequently exposed to sunlight.
Stage 1:
Stage 1 cancers include one or fewer high-risk characteristics. These are generally less than 2 cm in size and have not spread to adjacent lymph nodes or organs.
Stage 2:
A tumor of any size with two or more high risk traits, as well as one that is larger than 2 cm in diameter and has not spread to adjacent lymph nodes or organs.
Stage 3:
At this stage, cancer is defined as having progressed to one neighboring lymph node or the face bones without affecting other organs.
Stage 4:
Stage 4 cancers can range in size, include at least one lymph node greater than 3 cm, and may have migrated to the bones or other internal organs.
7. How can you prevent Skin Cancer?
The majority of skin cancers are brought on by excessive Ultraviolet radiation exposure. Natural sunlight, tanning beds, and even sun lamps emit UV rays. Skin cells can be harmed by these radiations.

Skin Safety from Sun:
All year long and not just in the summer, it’s important to protect yourself from UV radiation. On cloudy days, UV rays can still get to you by reflecting off water, cement, sand, and snow.
- Stick to the shadows.
- Protect your arms and legs with clothing.
- Protect your face, head, ears, and neck from the sun if you are sensitive.
- Use sunglasses that can prevent UVA and UVB radiation.
- Carry a sunscreen with a Sun Protection Factor of 15 or higher.
Be Safe from Indoor Tanning:
If you tan indoors, then you are exposed to a lot of UV rays by utilizing tanning beds, booths, sunbeds, or sunlamps. Long-term exposure to UV radiation can result in cataracts, skin cancer, and eye cancer.
Note that health is not reflected in a tan. But in fact, the skin produces more melanin when UV rays hit the inner layer of the skin. The pigment melanin gives skin its color. It progresses to the surface of the skin and becomes noticeable as a tan. Any alteration in skin tone following UV exposure that might be a burn or a tan indicates an alarm rather than health.
How Punarjan Ayurveda Treats Skin Cancer?
Punarjan Ayurveda creates hope in the realm of skin cancer treatment. We dive deep into the profound wisdom of Ayurvedic principles so that we can provide the best cancer healing. This transformative methodology is in fact a contrast to conventional symptom-focused treatments simultaneously being a complementary treatment. At the core of Punarjan Ayurveda’s treatment program, we load it with meticulously crafted ayurvedic interventions. Formulations of herbal medicines, detoxification therapies, dietary recalibrations, and lifestyle amendments make our therapy.
Rasayana ayurveda is nature’s wonder and it reverberates within the essence of Punarjan Ayurveda’s healing efficiency. Embracing the natural powers, this innovative methodology weaves together the prowess of rare herbs including Neem, Turmeric, Aloe Vera, and Manjishtha. These botanical marvels, have potent anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and skin-revitalizing properties, not only target the malignant intruders but also nourish and replenish the skin. Punarjan Ayurveda is a steadfast proponent of holistic living. Our team of experts meticulously explore solutions for stress management, harmonious lifestyle, and the best nourishing dietary forms. These act as essential pillars of support for the innate capacity of your body on the arduous journey of recovery.
We are here to stand on the side of cancer sufferers where ancient wisdom and modern innovation converge. Let us start a transformative journey, where the shadows of skin cancer vanish.
Our Skin Cancer/Melanoma Cancer Survivor Stories
What are 2 signs of skin cancer?
Two signs of skin cancer to watch out for are:
A mole or other skin growth growing, asymmetrical, or changing color. Many things can cause this.
A chronic wound or sore may cause itchy, dry, or crusty skin for no apparent reason.
What foods prevent skin cancer?
Incorporating these nutrients reduces skin cancer risk.
Fruits and Vegetables: To maximize health advantages, eat more bell peppers, carrots, oranges, berries, and leafy greens.
Fish Rich in Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Salmon, prawns, and sardines are omega-3-rich fish. They’re fine.
Green Tea: Antioxidants shield your skin from UV radiation, preventing cancer.
Nuts and Seeds: Chia seeds, almonds, hazelnuts, and flax seeds make great snacks.
Tomatoes: Tomatoes enhance many recipes. Lycopene reduces skin cancer.
What is skin cancer’s first symptom?
Skin cancer often first appears as a skin alteration. New moles, mole changes, and unhealed wounds can indicate this.
Can skin cancer be cured?
Skin cancer is treatable and possibly curable if found early. Early detection improves treatment outcomes. If you find new moles, changes in their size, shape, color, or other questionable changes, consult a doctor immediately.
Where does skin cancer start from?
Skin cancer is linked to skin cells. It usually begins with skin cells multiplying uncontrollably. These growths may be malignant or benign. Protect your skin from UV radiation and check it often for abnormalities to detect skin cancer early.
How to avoid skin cancer?
Skin cancer is a devastating disease. We may easily limit exposure and improve skin safety. Basic suggestions:
Shield yourself from the sun
Apply sunscreen diligently
Cover up with protective clothing.
Wear sunglasses
Avoid tanning beds and sunlamps.
Perform regular skin self-examinations
Seek shade during peak UV hours
Does skin cancer spread?
Skin cancer is deadly. Skin cancer spreads by “metastasis” to other organs. It may have been cardiovascular or lymphatic. Early skin cancer diagnosis and treatment prevent complications and disease development.

